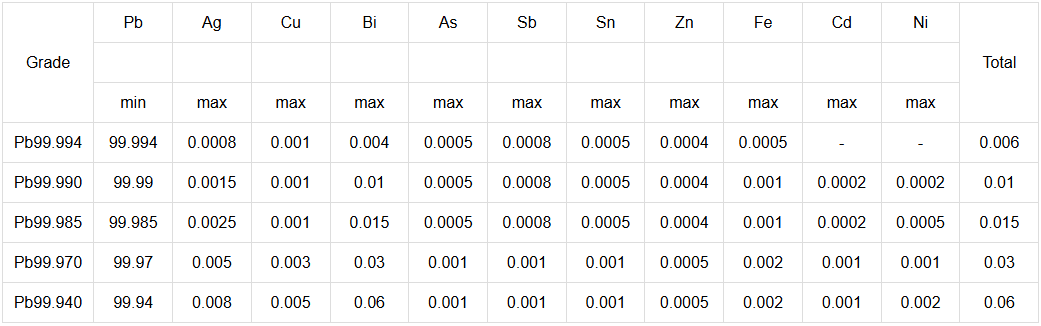
Description
Lead ingots are solid metal materials made from high-purity refined lead, typically cast in cylindrical or rectangular shapes. They possess excellent flexibility, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity, making them widely used across industries such as electronics, chemical engineering, medical treatment, and construction. Lead ingots are classified into two main types: pure lead ingots and alloy lead ingots. Pure lead ingots are primarily used for radiation shielding, vibration damping, and noise protection, while alloy lead ingots incorporate elements like tin, copper, and antimony to enhance properties such as strength, hardness, and wear resistance. These ingots come in various specifications and sizes, commonly weighing between 25kg and 50kg with approximate dimensions of 650mm by 150mm by 100mm, but can be customized to meet specific customer requirements. The material’s corrosion resistance ensures durability in chemically aggressive environments, while its high density and flexibility make it suitable for shielding and manufacturing applications. Lead ingots are critical components in electronics for grounding and shielding, medical equipment for radiation protection, chemical industry linings, construction waterproofing, and battery plate manufacturing. Overall, lead ingots offer broad application potential with high reliability and market demand in diverse industrial sectors.
Technical Details